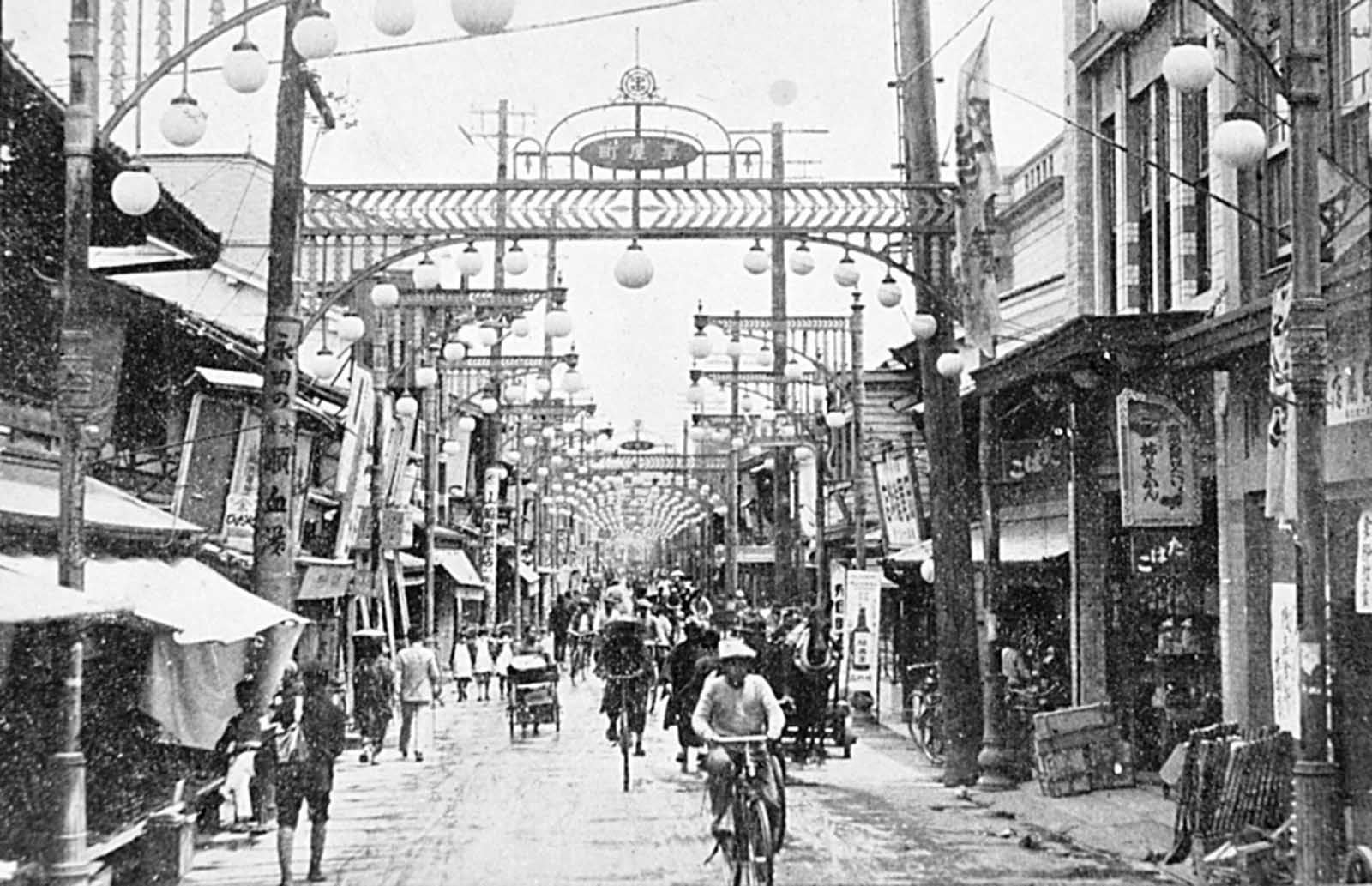
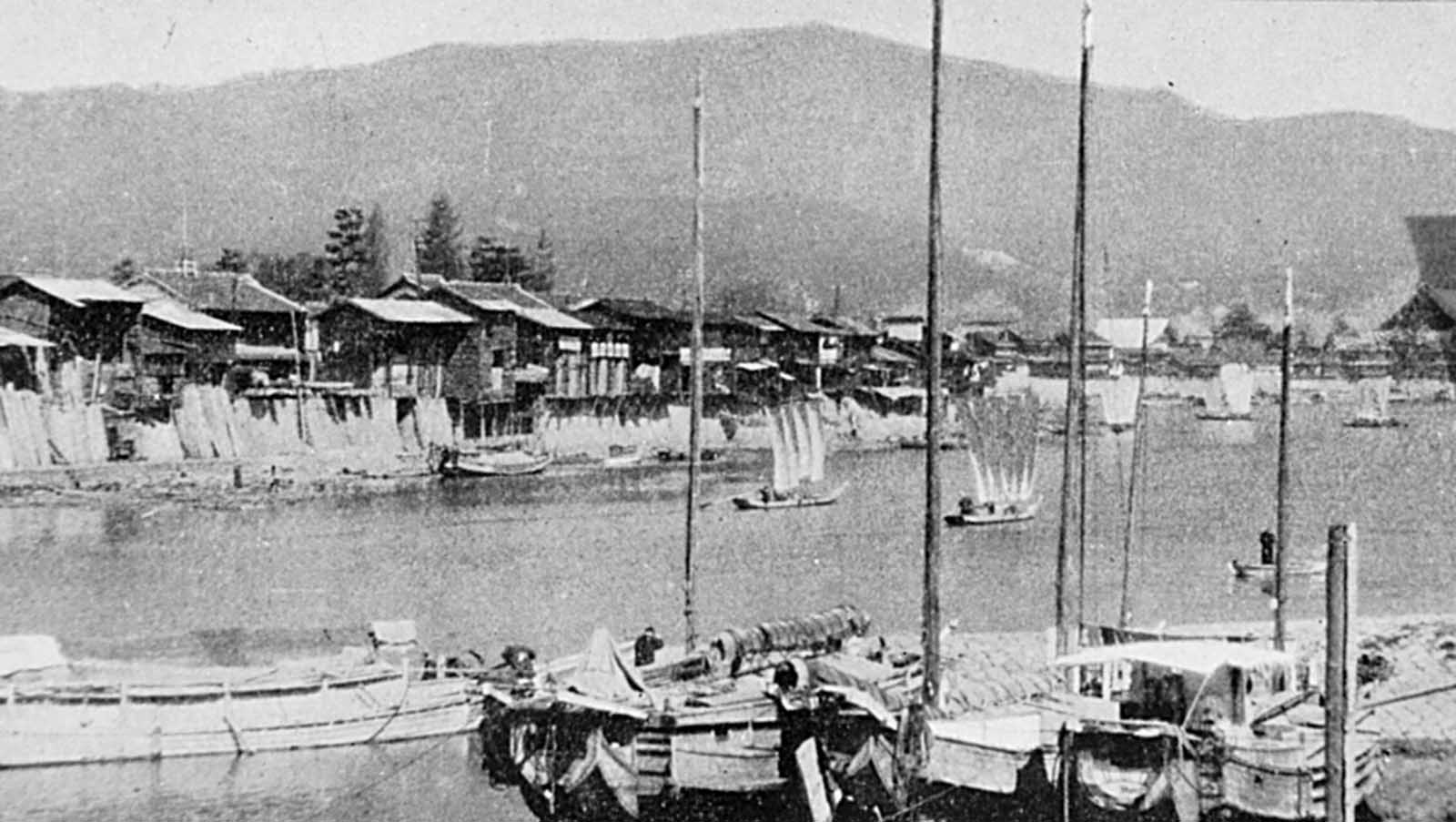
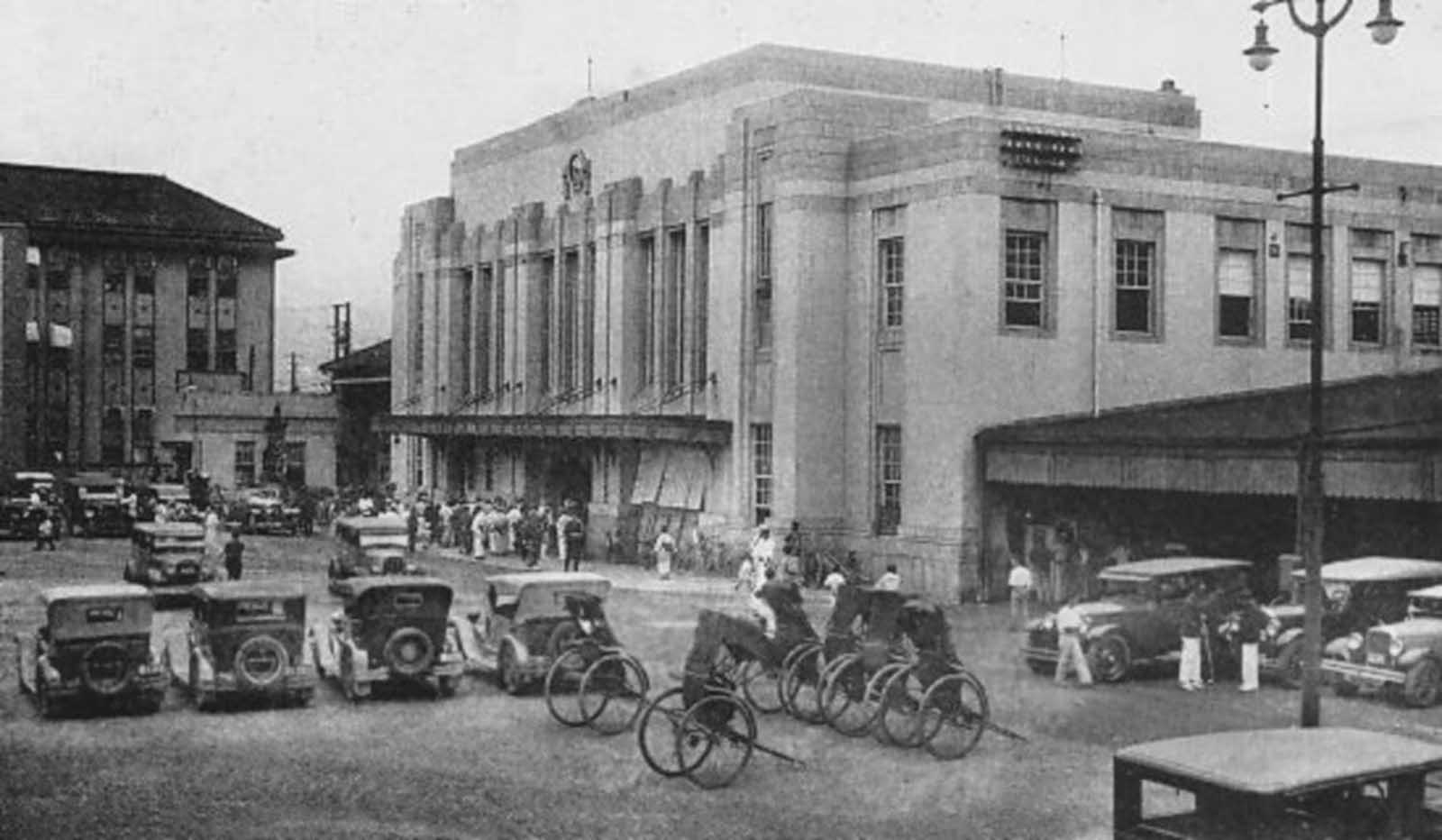
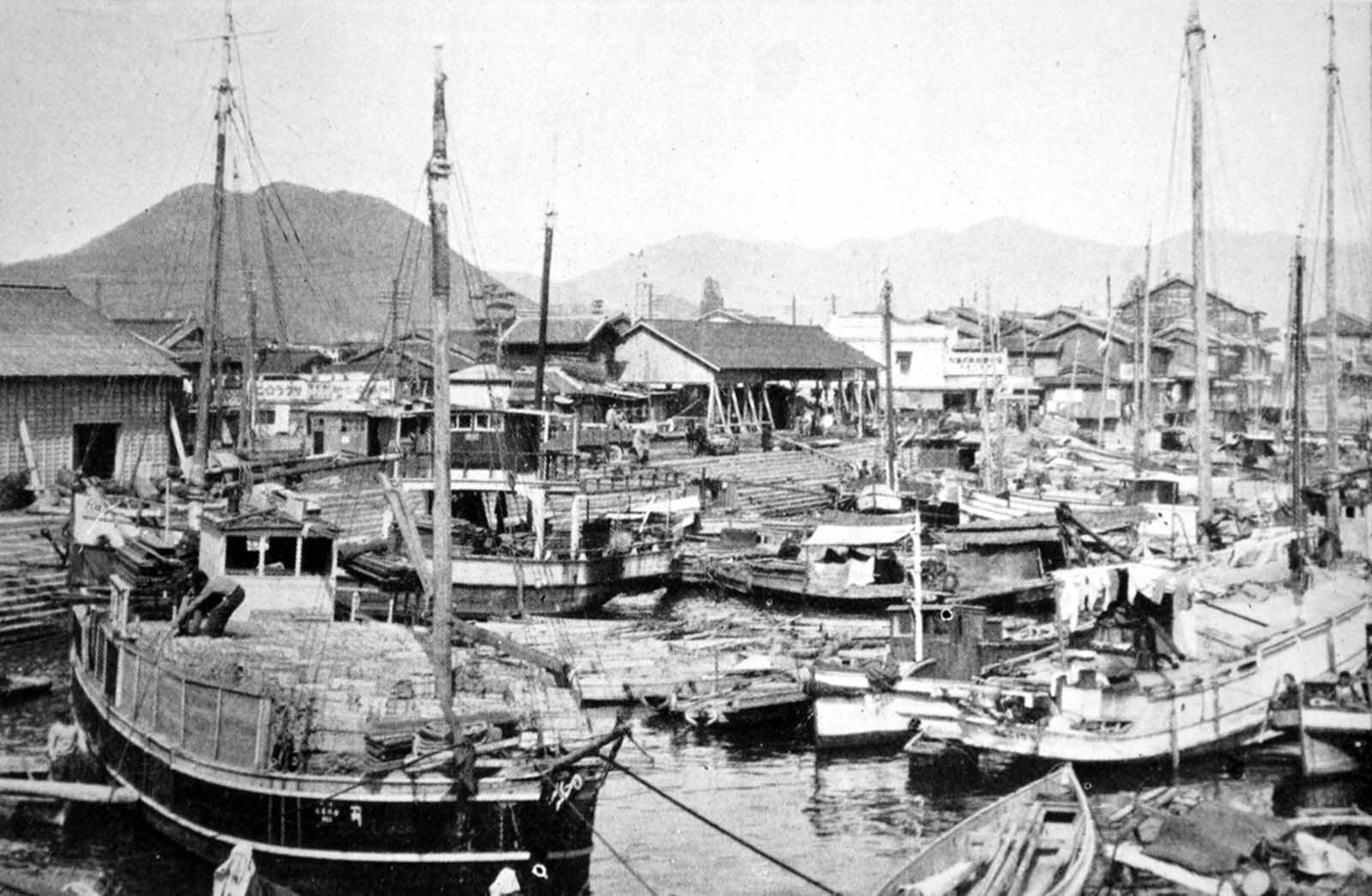
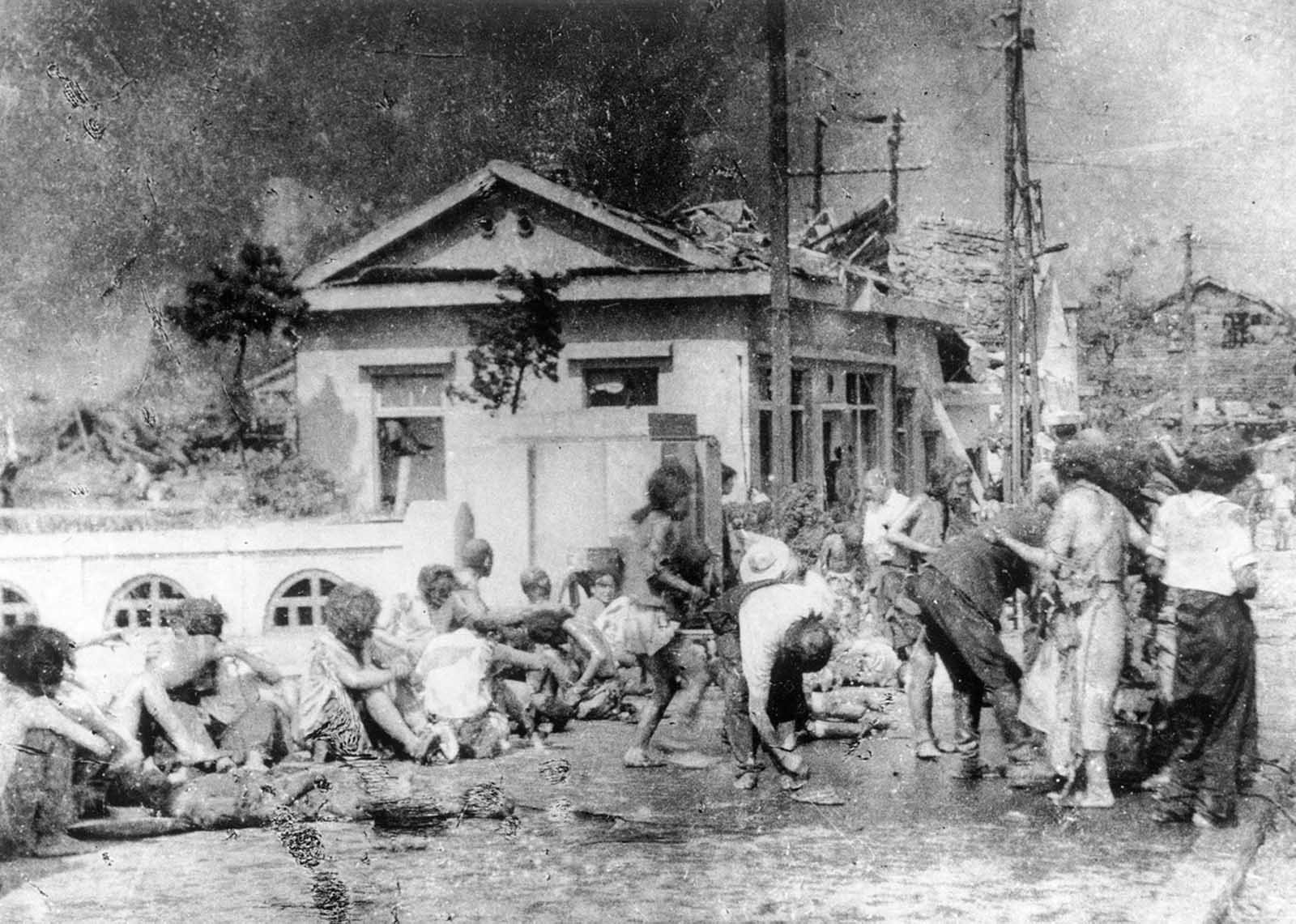
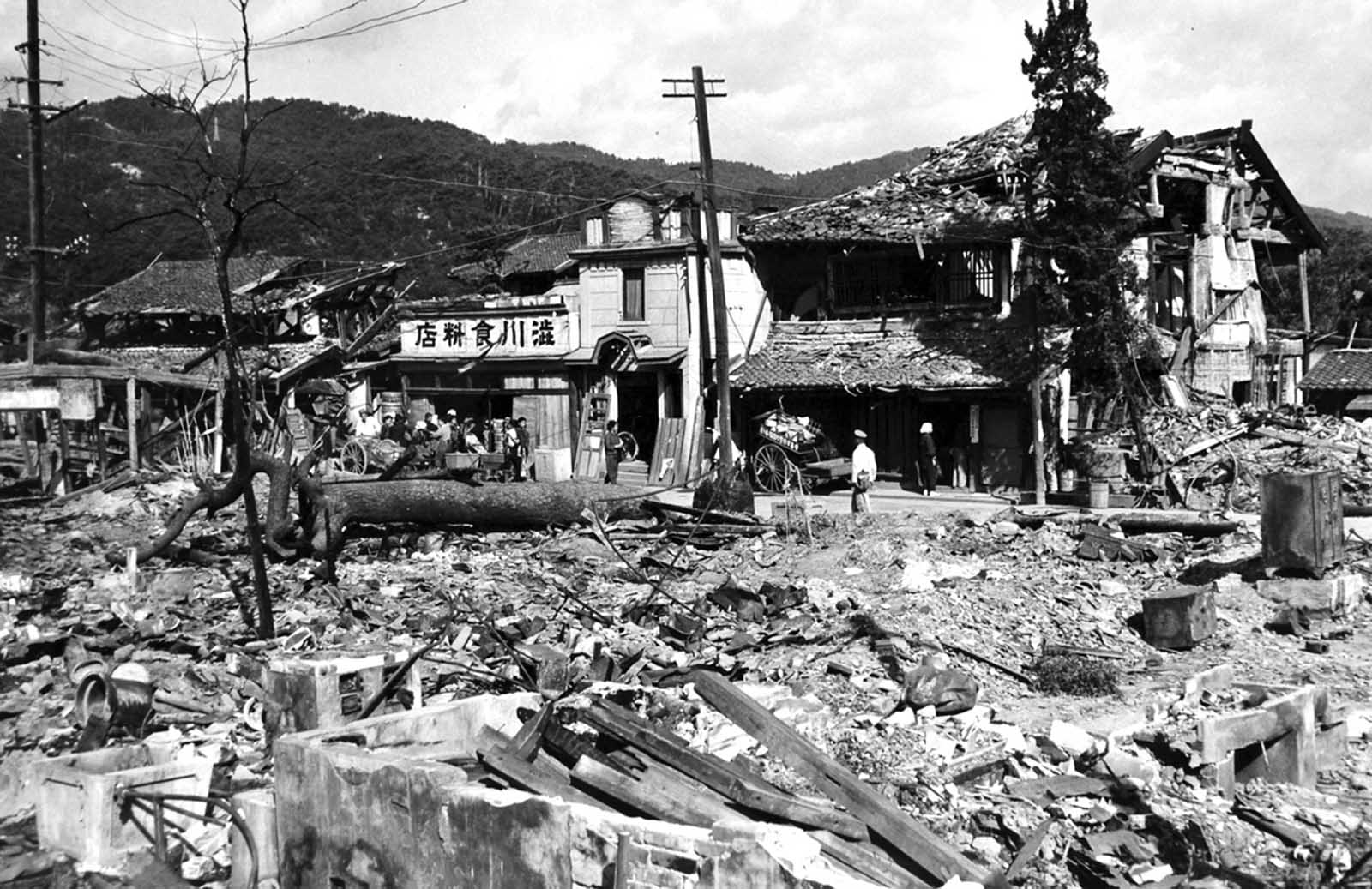
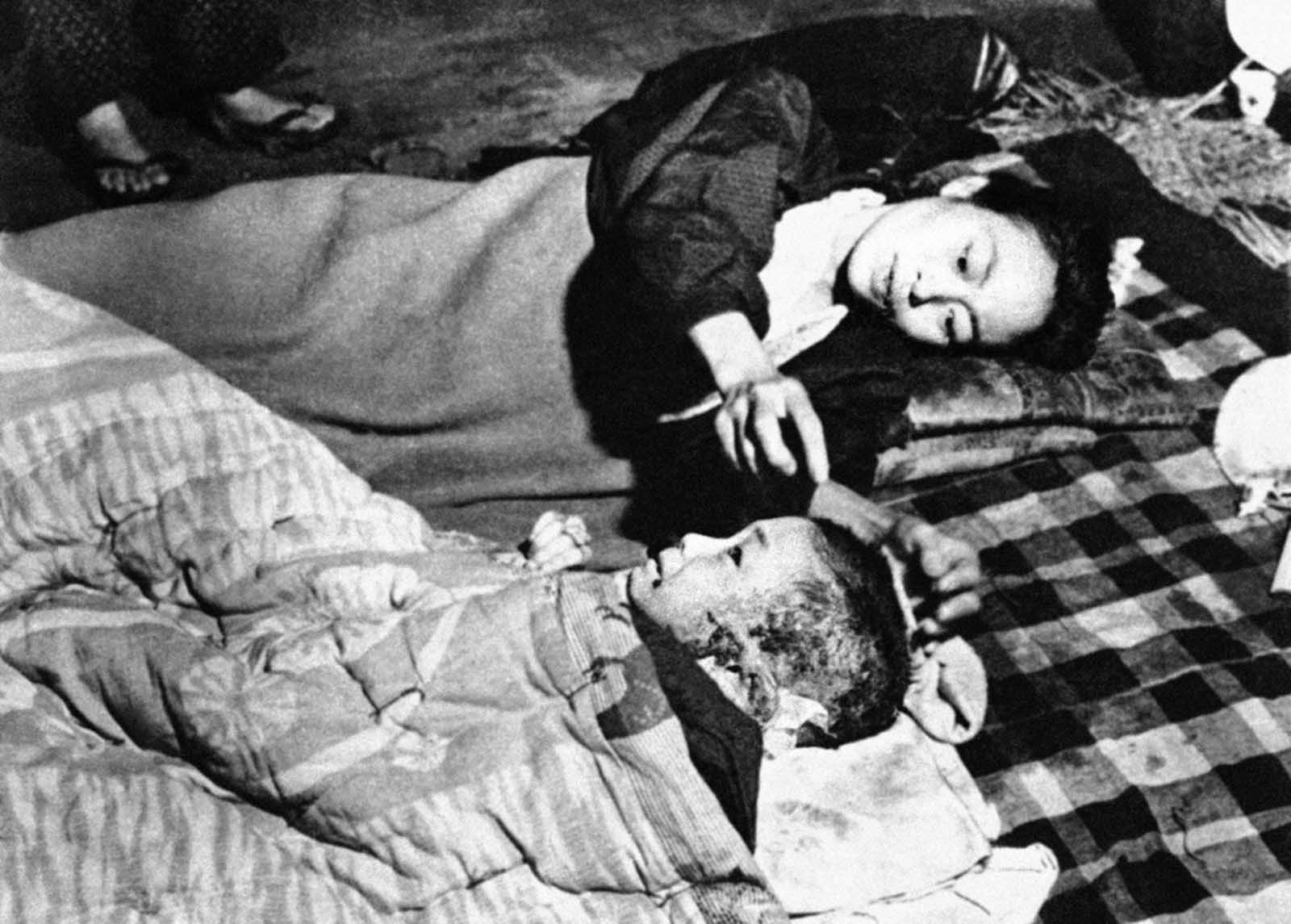
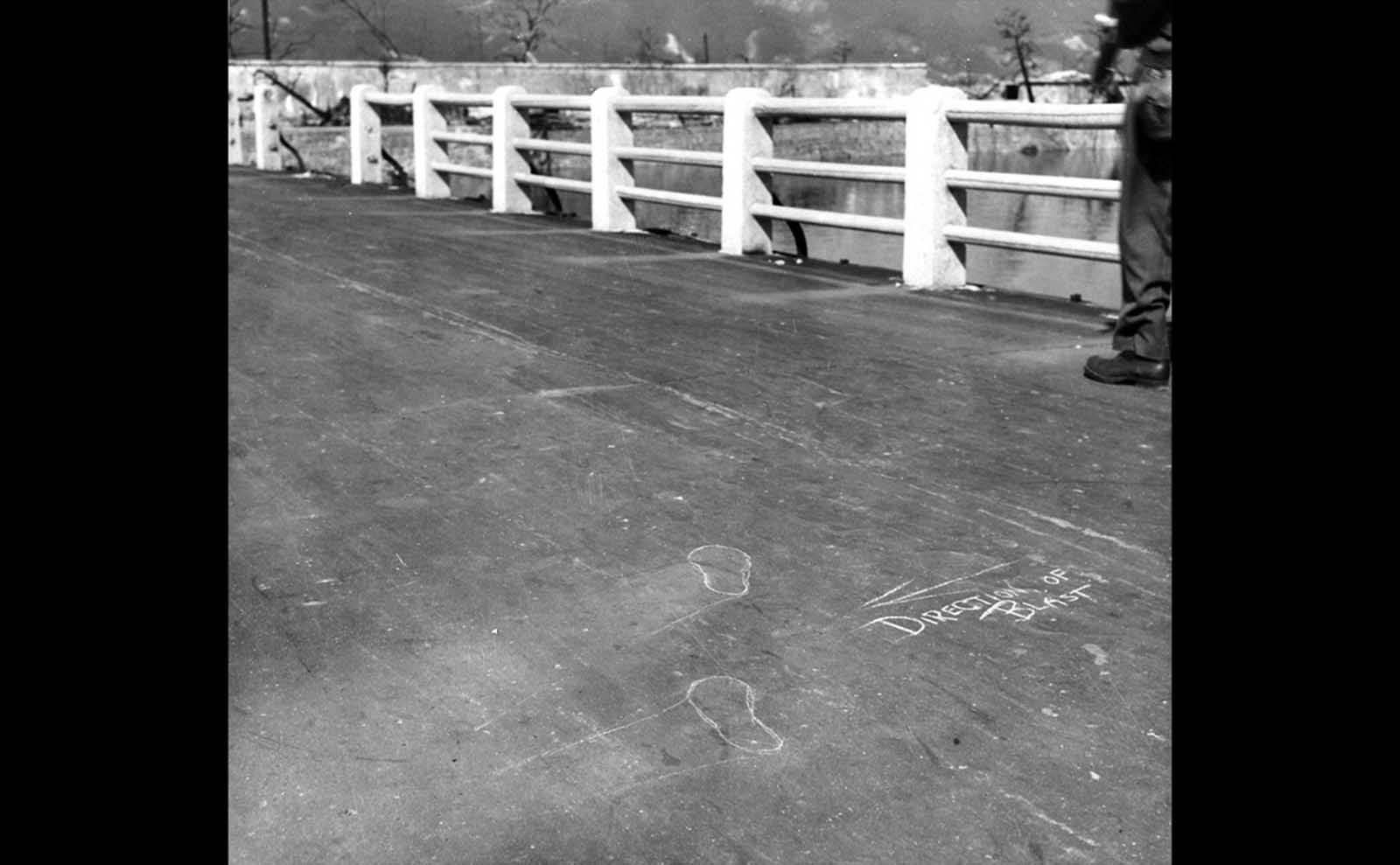
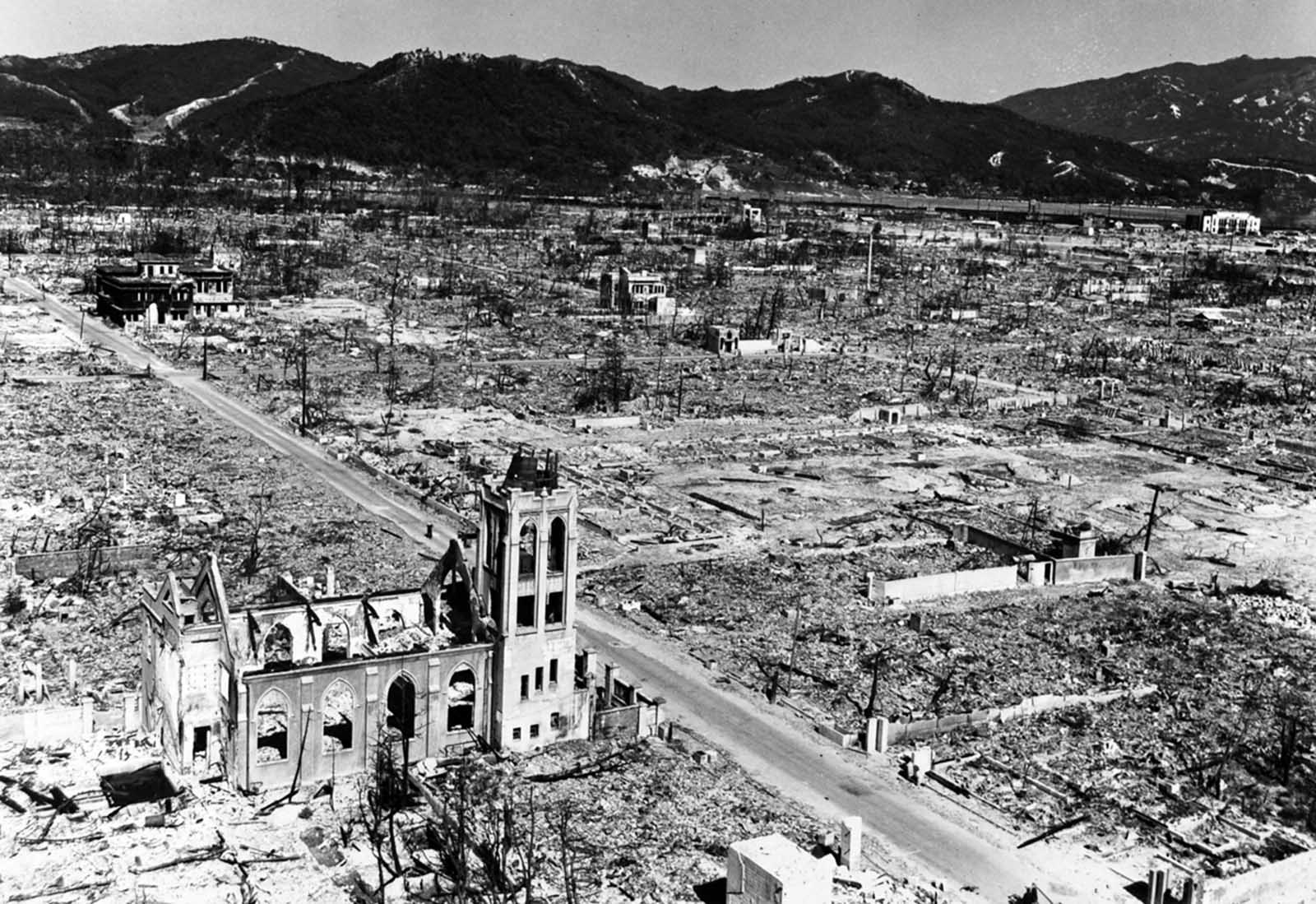
Hiroshima was a minor supply and logistics base for the Japanese military, but it also had large stockpiles of military supplies. The city was also a communications center, a key port for shipping, and an assembly area for troops. It was a beehive of war industry, manufacturing parts for planes and boats, for bombs, rifles, and handguns; children were shown how to construct and hurl gasoline bombs and the wheelchair-bound and bedridden were assembling booby traps to be planted in the beaches of Kyushu. A new slogan appeared on the walls of Hiroshima: “FORGET SELF! ALL OUT FOR YOUR COUNTRY!”. It was also the second-largest city in Japan after Kyoto that was still undamaged by air raids. The center of the city contained several reinforced concrete buildings and lighter structures. Outside the center, the area was congested by a dense collection of small timber-made workshops set among Japanese houses. A few larger industrial plants lay near the outskirts of the city. The houses were constructed of timber with tile roofs, and many of the industrial buildings were also built around timber frames. The city as a whole was highly susceptible to fire damage. The population of Hiroshima had reached a peak of over 381,000 earlier in the war but prior to the atomic bombing, the population had steadily decreased because of a systematic evacuation ordered by the Japanese government. At the time of the attack, the population was approximately 340,000–350,000. Residents wondered why Hiroshima had been spared destruction by firebombing. Some speculated that the city was to be saved for U.S. occupation headquarters, others thought perhaps their relatives in Hawaii and California had petitioned the U.S. government to avoid bombing Hiroshima. More realistic city officials had ordered buildings torn down to create long, straight firebreaks, beginning in 1944. Firebreaks continued to be expanded and extended up to the morning of August 6, 1945. On August 6, the U.S. dropped a uranium gun-type (Little Boy) bomb on Hiroshima, and American President Harry S. Truman called for Japan’s surrender, warning it to “expect a rain of ruin from the air, the like of which has never been seen on this earth”. On Monday, August 6, 1945, at 8:15 a.m., the nuclear weapon “Little Boy” was dropped on Hiroshima by an American B-29 bomber, the Enola Gay, flown by Colonel Paul Tibbets, directly killing an estimated 70,000 people, including 20,000 Japanese combatants and 2,000 Korean slave laborers. By the end of the year, injury and radiation brought the total number of deaths to 90,000–166,000. The population before the bombing was around 340,000 to 350,000. About 70% of the city’s buildings were destroyed, and another 7% severely damaged. The radiation from the explosion created permanent shadows As thermal radiation travels in straight lines from the fireball, any opaque object in its path produces a ‘nuclear shadow’. Hence the radiation produced permanent nuclear shadows of objects and even people around the sites which can be seen even today. The heat of the explosion instantly vaporized the bodies of people in the near vicinity but left their shadows. About 12 cyanide pills were kept in the cockpit of the Enola Gay (plane carrying A-bomb). The pilots were instructed to take them if the mission was compromised during the bombing of Hiroshima. Hiroshima Peace Flame will be lit till all nuclear bombs are destroyed. Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park was built on the open field created by the explosion. It is dedicated to the legacy of Hiroshima being the first city on earth to experience the horrors of a nuclear attack, and to the memories of the direct and indirect victims of the bombing. One of its monuments is the Peace Flame which was lit in 1964 and will continue to do so until all nuclear weapons on the planet are destroyed. (Photo credit: US Army Archives / National Archives / Library of Congress). Notify me of new posts by email.
Δ Subscribe